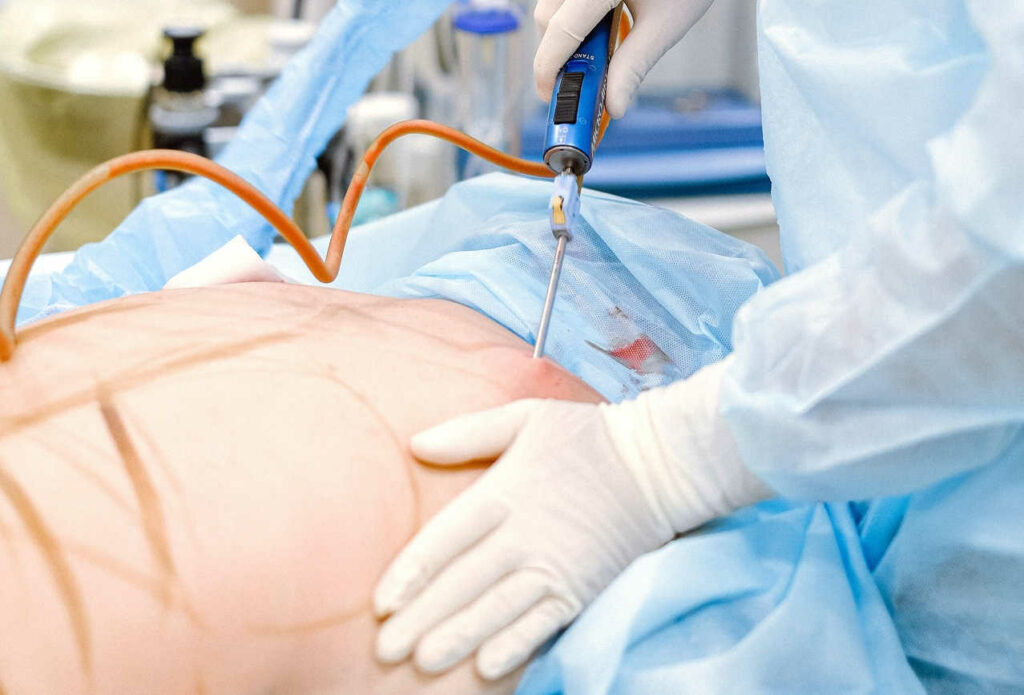
Liposuction is the most performed aesthetic surgery in the world. It is also the well-known and popular procedure that sculpts areas of the body with excess fat, streamlining, slimming and contouring the body. A tummy tuck, also known as abdominoplasty, is a plastic surgery procedure that aims to firm, flatten, and smooth the abdomen. During this surgery, a plastic surgeon removes excess fat and skin and tightens the abdominal muscles. The tummy tuck is not like liposuction. The two are often combined because the primary objective of abdominoplasty is to tighten muscle tissue, not remove fat. In combination, liposuction and a tummy tuck can significantly improve abdominal contours.
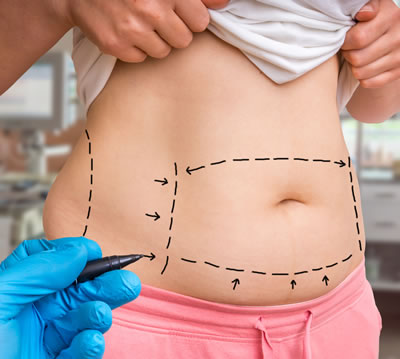
A tummy tuck can be ruined. Patients should not count on their tummy tuck to last indefinitely if they do not maintain healthy lifestyle habits after their procedure. Weight gain can still occur and stretch the abdominal muscles. Pregnancy may also diminish the contouring achieved with a tummy tuck; hence it is highly recommended to postpone this procedure until after one’s family is complete.
Although, these procedures are appealing and appears more aesthetic, there are hidden disadvantages, when it comes to metabolic health.
Body composition differs significantly according to the sex. Men tend to carry less fat composition (10-20%) whereas women have a greater fat composition (18-30%) because of the female sex hormones which promote fat storage. Estrogen promotes hyperplasia (increase in number) of fat cells and its deposition mainly in the gluteo-femoral (hips & butts) region in the subcutaneous space. Thus, women of reproductive age groups can expand the subcutaneous adipose fat depot without becoming metabolically sick. It is evident that the Subcutaneous Fat threshold (beyond which it gets deposited in the visceral space) is much higher in women compared to men. Women tend to suffer from metabolic conditions at least 400 % less compared to men because of the same reason. But once they attain menopause, the protective effect of estrogen to store more subcutaneous fat is lost and they start depositing fat in the visceral space and tend to become metabolically unhealthy, particularly if they are following a poor dietary lifestyle and sedentarism as well as having a poor muscle mass (sarcopenia).
Subcutaneous Fat is a metabolic advantage. Evolutionarily, our human race survived droughts and famines because we are able to store the excess energy in the form of fat for future use (during periods of adversity). We are no longer facing the times of food scarcity or famine in the last 4 to 5 decades and we are living in a world of surplus- simply like “cactus in the rainforest”. Unfortunately, in the last 5 decades the human race is suffering from surplus nutrition developing overweight and obesity.
The fats that are getting stored in the subcutaneous space from head to toe are good fats because they secrete anti-inflammatory adipokines that modulate metabolism favorably. But once the capacity to store fat becomes saturated, they become hypoxic and secrete proinflammatory cytokines for angiogenesis (establishing new blood vessels) for the hypertrophied fat cells as a compensatory mechanism for their survival. The hypertrophied fat cells become insulin resistant, now promoting lipolysis increasing the free fatty acids in the circulation. Now the whole body tend to suffer from insulin resistance because of proinflammatory cytokines and excess free fatty acids in the circulation. Now, the fat storage occurs in the visceral space and also throughout the body including vital organs like liver, pancreas, heart, kidneys and blood vessels supplying them.

Generally, Subcutaneous fat expands by hyperplasia (increasing number of fat cells) whereas visceral fat undergoes hypertrophy (increase in size). It is not the fat that you see (pinchable fats or external obesity) but the invisible fat (internal obesity) that you cannot see, kills you slowly. The external (subcutaneous) obesity is a metabolic buffer of positive energy balance which protects against insulin resistance until the personal fat threshold is overwhelmed. The internal obesity in the visceral space particularly in the liver promotes insulin resistance and affects cardio-metabolic health adversely over a period of time.
The subcutaneous fat in the abdominal region is called the stubborn fat. The first fat to get mobilized under fasting or low insulin dietary protocol is the visceral fat which is metabolically active and also being resistant to the anti-lipolytic action of insulin. Hence the visceral fat in the abdominal area gets mobilized easily but the subcutaneous fat in the abdominal area which is actually benign is the last to get mobilized. Therefore, it is usually called as the stubborn fat. The ectopic fat (including the visceral fat) is preferentially mobilized compared to the subcutaneous fat and hence mobilization of subcutaneous fat takes a longer time for it to be used as a source of energy whether by fasting or dieting or regular physical activities. It is not a stubborn fat anymore and we can achieve aesthetic look even without any surgical intervention or liposuction.
Generally Fat cell Numbers in Teen years linger for a lifetime. A normal person has between 25-35 billion fat cells, but this number can increase (hyperplasia, more so in women under the influence of estrogen) in times of excessive weight gain, to as many as 100-150 billion cells. The number of fat cells in the body remains constant after their formation; the cells just expand (hypertrophy, more so in males) and shrink in size during weight gain and weight loss respectively. Fat cells have an excellent capacity to shrink and expand in accordance with the energy balance. The radius of the fat cells can increase up to 20 times which then translates into 8000 times increase in its volume.
Personalized dietary protocols to change the body composition (for example, increasing the protein intake and reducing the energy in the form of both carbs and fats along with micronutrient rich and fiber rich diet) along with Fasting and regular workouts, helps in melting down the so-called stubborn fat in the context of low insulin levels. Low insulin level causes lipolysis (breakdown of fats) and hence the subcutaneous fat stores are used up as a source of energy. It is quite possible to achieve aesthetic appearance naturally with a healthy lifestyle. The fat cells are better shrunken by this holistic approach rather than to remove them by liposuction or tummy tucks.
The safe limit for fat removal through liposuction is typically around 6-8 pounds (equivalent to 3-4 liters). Going beyond this limit increases the potential risks of complications. Liposuction cannot be considered a weight loss surgery as it does not reduce your overall weight considerably. Instead, this surgical procedure targets excess fat stores in precise areas of the body and improves an individual’s shape or appearance. Only the fat under the skin can be removed during liposuction, not the internal fat that surrounds our organs which is related to Insulin resistance -related medical problems. The main goal of liposuction is to shape the body by removing inches. Many patients can lose 1-3 inches depending on the treatment area and the amount of fat removed.
In abdominoplasty (tummy tuck), the typical recipient loses between 4-15 pounds depending on how much excess abdominal skin there is, how much fat in the abdominal region and the type of abdominoplasty selected. Again, tummy tucks are not a weight loss solution. To qualify for the procedure, you must be at or close to your ideal weight. Although the fat percentage of fat mass can go substantially from 30% to 20% following the procedure, the cardiometabolic risk stays the same; perhaps they have increased risk of developing cardiometabolic conditions over a period of time since they have lost a significant fat depo in the subcutaneous space.
These procedures are mainly done in younger and middle-aged women, mainly the reproductive age groups. Most of the fat cells throughout the body under normal conditions are smaller and expand by hyperplasia (increasing their number) and not by hypertrophy (which causes insulin resistance when it reaches the upper threshold limit). The hyperplastic baby fat cells in the subcutaneous region throughout the body are a metabolic advantage to the premenopausal women which act like a shield protecting against the development of insulin resistance and metabolic disorders.
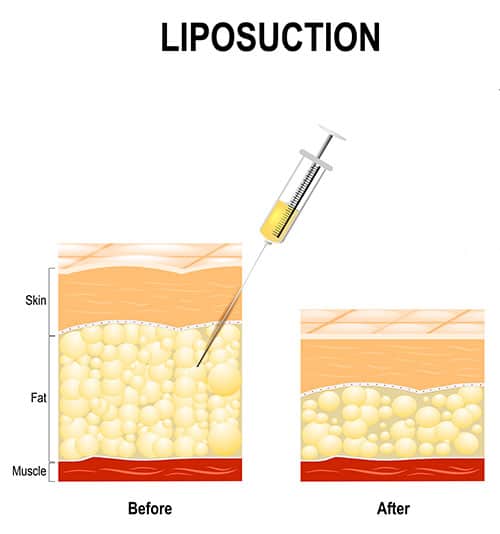
When the fat cells are considerably removed most of them being in the small & hyperplastic stage, the total number of healthy fat cells which acts as a depot for energy storage decreases. In other words, the Personal Fat Threshold of the person decreases after these procedures. Now when there is positive energy balance, the left-out fat cells have limited capacity to expand by hyperplasia and over a period of time, it expands by hypertrophy and hence they have increased risk of developing insulin resistance. Whenever the personal fat threshold gets reduced, the fat deposition eventually happens in the visceral space leading to metabolic related disorders.
Shrinking the fat cells by comprehensive holistic metabolic approach of eating healthy, staying in fat-burning mode for most part of the day, fasting and regular physical activities actually help in keeping the fat cell intact and healthy whereas removing or sucking out fat cells in the subcutaneous space by these procedures could lead to reduced number of fat cells, overall. To summarize, the good subcutaneous fat gets removed leaving behind the dangerous and bad visceral fat untouched. It is very important to maintain ideal body weight after the procedures by eating right and involving themselves in regular physical activities to prevent any such metabolic complications.
“Nothing makes a woman more beautiful than the belief that she is beautiful.”