Knee replacement surgery is one of the major surgeries done in most of the tertiary care centers. Osteoarthritis is classically referred to as the degenerative changes because of wear & tear. But is it really so? OA knee seen in the elderly is increasingly affecting even the middle aged nowadays, tells you a different story. Obesity, together with aging and injury, is among the main risk factors for osteoarthritis. Obesity-related osteoarthritis can affect not only the weight-bearing joints, but also the hands, suggesting a role for circulating mediators released by the adipose tissue and known as adipokines. Thus, osteoarthritis may have a systemic metabolic component. Evidence from both epidemiological and biological studies support the concept of metabolic osteoarthritis, defined as a broad clinical phenotype that includes obesity-related osteoarthritis. Thus, osteoarthritis can be related to metabolic syndrome or to an accumulation of metabolic abnormalities. In addition, studies have demonstrated associations linking osteoarthritis to several components of the metabolic syndrome, such as hypertension and type 2 diabetes, independently from obesity or any of the other known risk factors for osteoarthritis. Both in vitro and in vitro findings indicate a deleterious effect of lipid and glucose abnormalities on cartilage homeostasis. Chronic low-grade inflammation is a feature shared by osteoarthritis and metabolic disorders and may contribute to the genesis of both. Thus, osteoarthritis is emerging as a disease that has a variety of phenotypes including a metabolic phenotype as the predominant variety, in addition to the age-related and injury-related phenotypes.
In OA, the joint space is decreased due to damaged cartilage and bone spurs. The evolution of the Osteoarthritis disease process is characterized by cartilage degradation at least in part by proteolytic breakdown of macromolecules, in which MMPs play an important role. Further, fibrillation and erosion of the cartilage surface result in the release of molecular breakdown products into the synovial fluid. The phagocytosis of cartilage matrix breakdown products and other materials induces an inflammatory reaction in the synovial membrane, thereby resulting in local synthesis of proteases and proinflammatory cytokines.
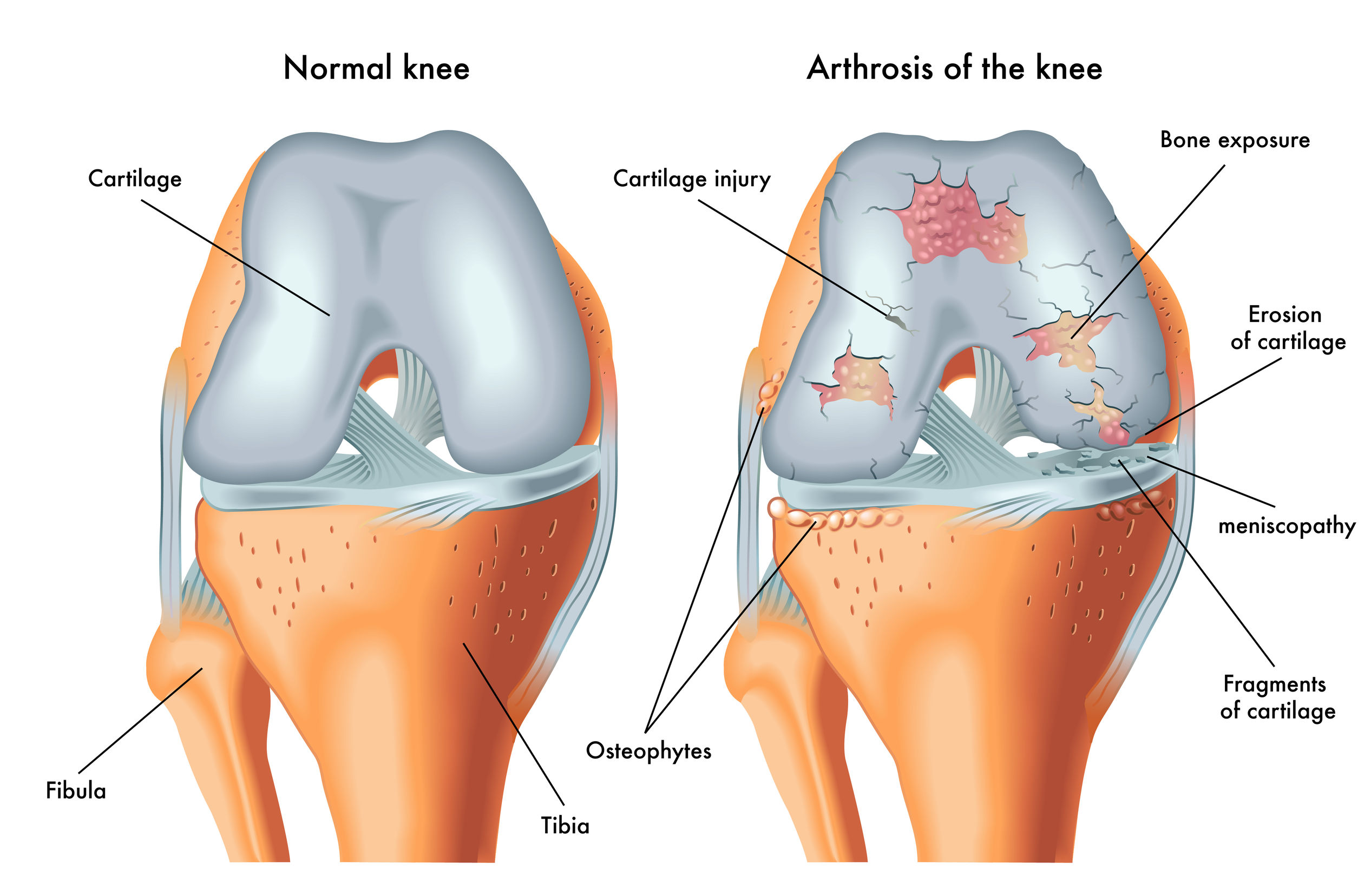
We all know that the modern diseases of civilization have been rampant in the last 40-50 years; so is the prevalence of OA. Can there be any correlation between these two? Interestingly the answer is a huge yes when we know the roots of the disease !! Most of the cardiometabolic disorders are rooted in Insulin Resistance. Careful evaluation of OA roots in insulin resistance!!! But it is hard to believe…
Let's dive deeper into the science of understanding the pathogenesis of OA. In the past, OA was viewed as a degenerative condition occurring in old age because of the wear and tear phenomenon. Recent scientific researches challenge this hypothesis and favour the inflammation associated with insulin resistance as the major causative factor in OA. Some proponents favour that it is a combination of mechanistic and inflammatory disorder associated with insulin resistance. Increased joint loading, adipose tissue inflammation and atherogenic dyslipidemia act synergistically to induce tissue damage in OA. Synovial Macrophage activation and the resulting inflammation links the Obesity with OA. In diabetes, synovial insulin resistance causes reduced anti-inflammatory and anti-catabolic effects of insulin.
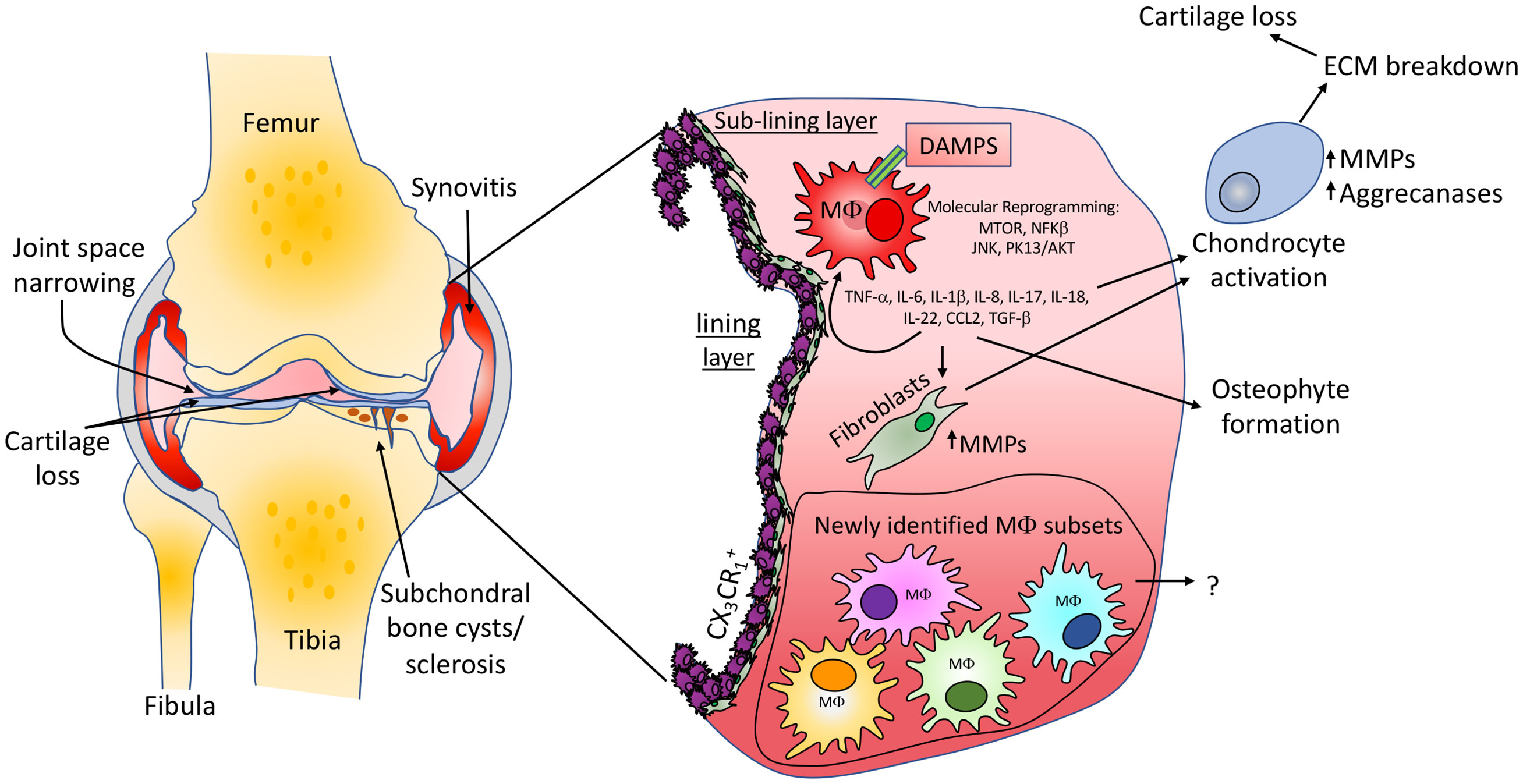
Hepatic Insulin resistance is associated with increased production of MMPs ( Matrix Metalloproteinases) ie., dissolve the extracellular matrix laid down by the bone forming cells called osteoblasts. Although normally MMPs are secreted constitutively from the liver in smaller amounts for homeostasis, their secretion is increased several times when someone suffers from insulin resistance. Other mediators in insulin resistance impacting joints are chronic low grade inflammation, proinflammatory cytokines like IL-6 and TNF-alpha. Now comes the question; are we treating it right ?
The various treatments which are widely available are NSAIDS to relieve pain ( actually it can destroy the joints on long term use). Calcium supplements and vit D normally considered to increase bone strength actually may increase the atherosclerotic burden !!!
1.Protein forms the backbone or the matrix, in which deposition of minerals like magnesium, calcium occurs. Hence protein rich foods are very much needed for healthier bones.
2. Vit D increases the absorption of calcium by several folds and hence calcium supplementation is usually not necessary for bone health.
3. Without Vit K2, the calcium absorbed is largely misdirected towards soft tissues and even arteries throughout the body increasing the atherosclerotic burden. Hence it is utmost essential to prescribe vit K2 whenever vit D3 is suggested to guide the absorbed calcium towards the bones. Vit K2 deposits calcium in the bones and takes away the calcium deposition from the arteries.
4. Magnesium supplementation mitigates chondrocyte apoptosis and facilitates chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation. Synergistic effect of Magnesium and probiotics in modulating the inflammatory milieu could help in the prevention and treatment of OA.
5. Vit C acts a cofactor in the hydroxylases which converts proline to hydroxy proline; Proline, hydroxyproline and Glycine form the basic structural components of collagen and its long-term deficiency causes impaired collagen synthesis and scurvy. Hence it is essential to supplement vit C for optimizing collagen synthesis.
An artificial knee joint has metal caps for the thigh bone and shine bone, and high-density plastic to replace damaged cartilage. Each of these artificial parts is called a prosthesis. Knee replacements surgery replaces parts of injured or worn-out knee joints. The surgery can help ease pain and make the knee work better. Recent research studies found that about a third of total knee replacements in the United States are inappropriate. The numbers could be considerably far higher in our country.
If a person is severely affected by osteoarthritis with poor quality of life impacting everyday activities, causing them patient to stay in the house more and avoiding outdoor activities. People who need knee replacement surgery usually have problems walking, climbing stairs and getting up out of chairs.However, the most common reason for knee replacement surgery is to ease pain caused by arthritis. Fortunately, in our holistic approach pain gets settled in a few weeks in most of the patients with OA by reversing insulin resistance with a micronutrient rich, anti-inflammatory diet and protocols. As a general rule, it avoids unnecessary surgical intervention.
knee replacement surgeries can be considered only if it is resistant to optimal conservative management.
Although Knee replacements are common and relatively safer procedures nowadays, the risk of having complications depends on your age and general health.
1. Blood clots or DVT (Deep Vein Thrombosis) and sometimes serious complications like pulmonary embolism.
2. Wound infections are less common, and they are treated with antibiotics but sometimes may require further surgeries.
3. Damage to nerves or tissues.
4. Problems with your new knee may be in bending the knee, ongoing pain and stiffness and instability which improve with physiotherapy and certain exercises.
5. Per-operative and postoperative anesthetic and drug adverse reactions.
Pain relief, improved joint function and joint stability are the main goals of treatment. The muscle weakness and muscle atrophy contribute to the disease process. So, rehabilitation and physiotherapy were often prescribed with the intention to alleviate pain and increase mobility. However, as exercise has to be performed on a regular basis in order to counteract muscle atrophy, continuous exercise programs are recommended in people with degenerative joint disease. Therapeutic exercise regimes either focus on muscle strengthening and stretching exercises or on aerobic activity which can be water based. Surgery should be reserved for those that have not responded appropriately to less invasive methods.
1.Maintaining Insulin sensitivity throughout your life.
2.Ensure your diet contains quality proteins in adequate amounts. Unfortunately, Indian subpopulation tend to have a deficit of 30-40% in their daily intake of proteins. People over 60 years actually require 1.5 times the normal protein requirement which is not met in most of the cases.
3.Micronutrient rich diet (vitamins, mineral, antioxidants, polyphenols)
4.Regular physical activity & exercise."Use it or else you lose it" (Bone is a dynamic structure - improving muscle mass and strength improve bone density and quality).
5.Ensure the TDS of drinking water in the optimal range of 200-300 (RO water with TDS less than 50 in most cases have the potential to leach out the minerals in the bones over a period of time).
"Preserve your joints before it is too late".
